RubyGem
Update Gems
Experienced developers use a few tricks to optimize the Ruby development environment and keep it up to date. It's best if everything is up to date before you start a new project.
Faster Gem Installation
By default, when you install gems, documentation files will be installed. Developers seldom use gem documentation files (they browse the web instead). Installing gem documentation files takes time, so many developers like to toggle the default so no documentation is installed.
Here's how to speed up gem installation by disabling the documentation step:
$ echo "gem: --no-document" >> ~/.gemrc
This adds the line gem: --no-document to a hidden .gemrc file in your home directory.

Check the gem manager
RubyGems is the package manager in Ruby. We use it to install software packages that add functionality to Ruby.
Check the installed gem manager version.
$ gem -v
3.2.3
You can check if a newer RubyGems version is available. Use gem update --system to upgrade the Ruby gem manager if your version is old:
$ gem update --system
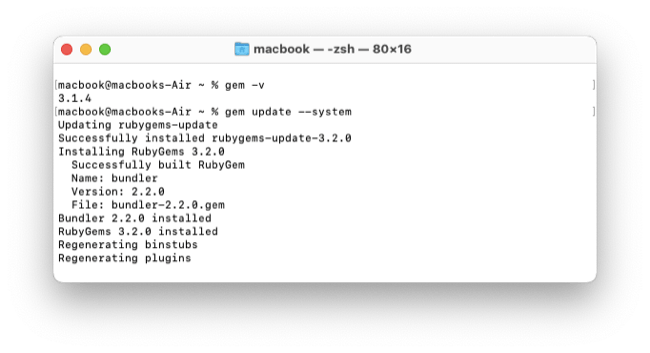
Mine: 3.4.12.
Updating gems
With Ruby, you’ve installed a collection of default gems that were current at the time of the Ruby release. It is likely some gems have been updated since the newest version of Ruby was released.
You can see a list of all gems installed with Ruby:
$ gem list
*** LOCAL GEMS ***
.
.
.
To get a list of gems that are outdated:
$ gem outdated
.
.
.
To update all stale gems:
$ gem update
Updating installed gems
.
.
.
You can track updates to gems at the RubyGems.org site by creating an account and visiting your dashboard.
Everything is ready. You can begin developing applications with Ruby.)
I stopped following Daniel Kehoe's amazing step-by-step guide here.
Next:
Deploying Ruby applications
Uninstalling Ruby
Troubleshooting
Where to get help